Windows System32 Catroot2 dberr.txt is a crucial file in the Windows operating system, responsible for storing error information related to the Windows Update process. Understanding the purpose and contents of this file is essential for troubleshooting and resolving update-related issues efficiently.
Recently, Fortect has become increasingly popular as a reliable and efficient way to address a wide range of PC issues. It's particularly favored for its user-friendly approach to diagnosing and fixing problems that can hinder a computer's performance, from system errors and malware to registry issues.
- Download and Install: Download Fortect from its official website by clicking here, and install it on your PC.
- Run a Scan and Review Results: Launch Fortect, conduct a system scan to identify issues, and review the scan results which detail the problems affecting your PC's performance.
- Repair and Optimize: Use Fortect's repair feature to fix the identified issues. For comprehensive repair options, consider subscribing to a premium plan. After repairing, the tool also aids in optimizing your PC for improved performance.
Troubleshooting Windows system32 Catroot2 folder
The Windows System32 Catroot2 folder is a special folder in the operating system that is used for cryptography and logging. Sometimes, users may encounter issues with this folder, resulting in errors like “dberr.txt” appearing.
To troubleshoot this issue, you can try several steps. First, open File Explorer and navigate to the System32 folder. Locate the Catroot2 folder and open it. Look for the “dberr.txt” file and delete it.
Next, open the Command Prompt or PowerShell as an administrator. Type “net stop cryptsvc” and press Enter. This will stop the Cryptographic Services. Then, type “ren %systemroot%\system32\catroot2 oldcatroot2” and press Enter. This will rename the Catroot2 folder.
After that, restart your computer. Windows will create a new Catroot2 folder automatically.
If the issue persists, you can try using System Restore or running the Windows Update Troubleshooter to fix any potential problems with Windows updates.
Updating system and drivers for resolving issues
To resolve issues with the Windows System32 Catroot2 dberr.txt file, it is recommended to update the system and drivers. This can often fix any compatibility problems or errors that may be causing the issue. To update the system, follow these steps:
1. Open File Explorer by pressing the Windows key + E.
2. Navigate to the “C:\Windows\System32” folder.
3. Look for the “Catroot2” folder and double-click on it.
4. Locate the “dberr.txt” file and delete it.
5. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
To update drivers, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + X and select “Device Manager.”
2. In the Device Manager window, expand the categories and find the drivers that need updating.
3. Right-click on the driver and select “Update driver.”
4. Choose the option to search automatically for updated driver software.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the update.
Updating the system and drivers can often resolve issues with the Windows System32 Catroot2 dberr.txt file.
python
# File Read Example
try:
with open("example.txt", "r") as file:
content = file.read()
print(content)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File not found!")
# File Write Example
try:
with open("example.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("This is an example text.")
print("File written successfully!")
except PermissionError:
print("Permission denied!")
# File Append Example
try:
with open("example.txt", "a") as file:
file.write("\nThis line is appended.")
print("File appended successfully!")
except PermissionError:
print("Permission denied!")
# File Delete Example
import os
try:
os.remove("example.txt")
print("File deleted successfully!")
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File not found!")
In this sample code, we demonstrate file read, write, append, and delete operations in Python using the file “example.txt”. You can modify the code to work with different file names or extensions as per your requirements.
Restoring Windows system and replacing dberr.txt file
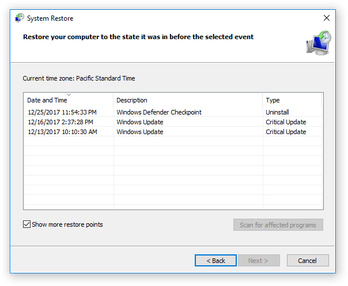
To restore your Windows system and replace the dberr.txt file in Windows System32 Catroot2, follow these steps:
1. Boot your computer and open the Command Prompt by pressing the Control key + R, then typing “cmd.exe” and pressing Enter.
2. In the Command Prompt, navigate to the System32 folder by typing “cd C:\Windows\System32” and pressing Enter.
3. Locate the dberr.txt file in the Catroot2 folder. You can do this by typing “dir Catroot2\dberr.txt” and pressing Enter.
4. Once you’ve found the file, close any programs that may be using it.
5. Use the command “del Catroot2\dberr.txt” to delete the file. Confirm the deletion when prompted.
6. To replace the file, download a new copy of the dberr.txt file from a trusted source.
7. Copy the downloaded file to the Catroot2 folder by using the command “copy [path to downloaded file] Catroot2\dberr.txt” and pressing Enter.
8. Confirm the replacement when prompted.
9. Finally, restart your computer to complete the restoration process.