Welcome to the ultimate guide on resolving the dreaded Windows Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) errors. In this article, we delve into effective techniques and solutions to fix your PC’s blue screen issues, ensuring a smoother and more stable computing experience. Say goodbye to those frustrating crashes and join us on this journey to resolve Windows BSoD errors once and for all.
Recently, Fortect has become increasingly popular as a reliable and efficient way to address a wide range of PC issues. It's particularly favored for its user-friendly approach to diagnosing and fixing problems that can hinder a computer's performance, from system errors and malware to registry issues.
- Download and Install: Download Fortect from its official website by clicking here, and install it on your PC.
- Run a Scan and Review Results: Launch Fortect, conduct a system scan to identify issues, and review the scan results which detail the problems affecting your PC's performance.
- Repair and Optimize: Use Fortect's repair feature to fix the identified issues. For comprehensive repair options, consider subscribing to a premium plan. After repairing, the tool also aids in optimizing your PC for improved performance.
Understanding the Windows Blue Screen of Death
If you’re experiencing the Windows Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) on your PC, don’t panic. This system error message indicates a problem with your computer that needs to be resolved. Follow these steps to fix the issue:
1. Restart your computer in safe mode by pressing the F8 key during startup.
2. Once in safe mode, click on the Start button and search for “Blue Screen Troubleshooter.”
3. Open the troubleshooter and follow the on-screen instructions to diagnose and resolve the issue.
4. Check for any available driver updates for your hardware. You can do this through the Device Manager in the Control Panel.
5. If the BSoD persists, try repairing your operating system by using the Windows 10 installation media.
6. If none of these steps work, it may be necessary to seek professional help or contact Microsoft Support for further assistance.
Remember, the BSoD can be frustrating, but with the right steps and support, you can resolve the issue and get your PC back up and running smoothly.
Common Causes of the Blue Screen of Death
- Hardware Issues: Faulty RAM, overheating components, or incompatible hardware can trigger a Blue Screen of Death (BSoD).
- Driver Problems: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can lead to BSoD errors, especially after a Windows update.
- Software Conflicts: Conflicting software, such as incompatible antivirus programs or recently installed applications, can cause BSoD crashes.
- Operating System Errors: System files corruption, registry errors, or improper Windows installations can result in BSoD occurrences.

- Virus or Malware Infections: Malicious software can disrupt system processes and trigger BSoD errors.
- Hardware Driver Issues: Faulty or incompatible hardware drivers can cause BSoD crashes.

- Overclocking: Overclocking the CPU or GPU beyond stable limits can lead to BSoD errors.
- Insufficient Power Supply: Inadequate power supplied to the system components can cause BSoD crashes.
- Memory Issues: Faulty memory modules or incorrect memory settings can result in BSoD occurrences.
Steps to Fix the Blue Screen of Death on Windows
-
Restart your computer.
- Click on the Start button.
- Select Restart from the power options menu.
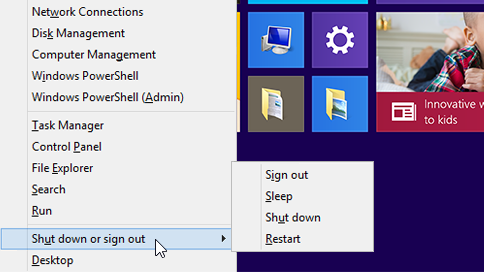
-
Boot into Safe Mode.
- Press and hold the Shift key while clicking on the Restart option.
- In the Advanced Startup menu, choose Safe Mode.

-
Uninstall recently installed software or updates.
- Open the Control Panel from the Start menu.
- Select Programs or Programs and Features.
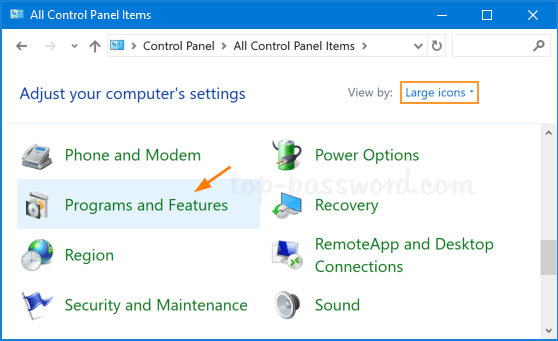
- Click on the Uninstall a program option.
- Find the recently installed software or update and click on Uninstall.
-
Update device drivers.
- Open the Device Manager by pressing Win+X and selecting Device Manager.
- Expand the categories to locate the device driver you want to update.
- Right-click on the device and choose Update driver.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the driver update.
-
Run a virus scan.
- Open your preferred antivirus software.
- Initiate a full system scan.

- Follow the prompts to remove any detected viruses or malware.
-
Check for hardware issues.
- Ensure all hardware connections are secure.
- Run a hardware diagnostic test if available.
- Consider consulting a professional if hardware issues persist.
-
Perform a system restore.
- Open the Control Panel from the Start menu.
- Select System and Security.
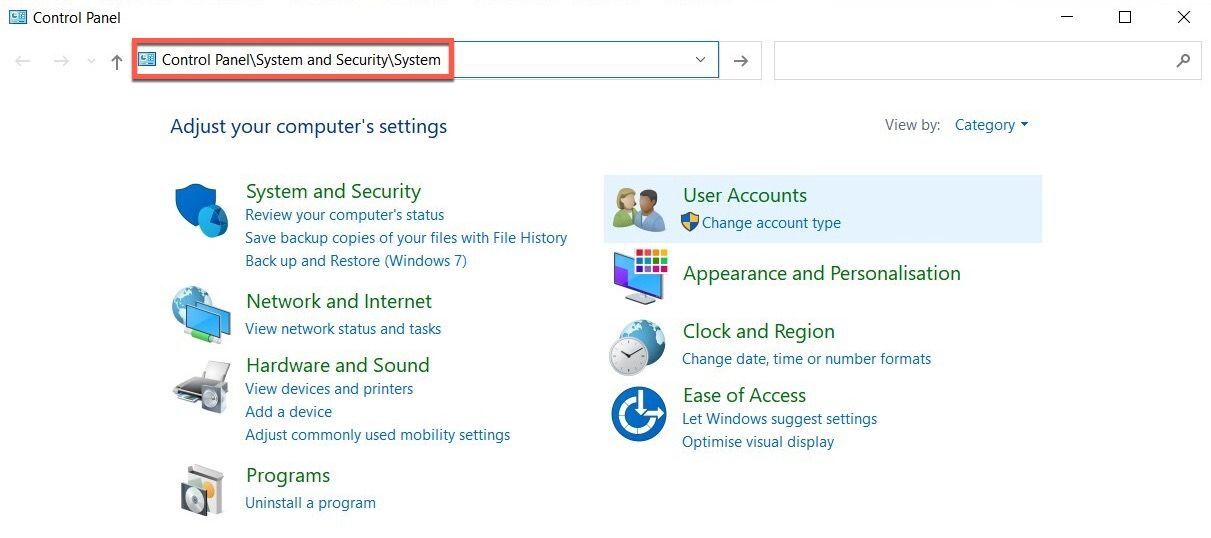
- Click on System.
- Choose System Protection and click on System Restore.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to restore your system to a previous point.
-
Reinstall Windows.
- Create a backup of your important files.
- Insert your Windows installation media.
- Restart your computer and boot from the installation media.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to reinstall Windows.
python
import time
def fix_blue_screen():
print("Initiating PC Blue Screen Fix...")
time.sleep(2) # Simulating a process delay
# Some code to fix blue screen issue goes here
# This could involve checking for faulty drivers, updating system files, etc.
# Since blue screen issues can have various causes, this example will simply print a success message
print("Blue screen issue fixed!")
# Running the blue screen fix tool
fix_blue_screen()
Please note that this is a basic example and does not provide an actual solution for fixing blue screen issues. Blue screen problems can be complex and have multiple causes, so it is essential to diagnose the specific issue before attempting any fixes. This example is just a demonstration of how you could structure a script for a blue screen fix tool.
Shutting Down and Disconnecting Devices
To shut down and disconnect devices, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key on your keyboard to open the Start menu.
2. Click on the Power icon located at the bottom left corner of the Start menu.
3. Select “Shut down” from the options to turn off your PC.
To disconnect devices:
1. Ensure that all external devices, such as printers or USB drives, are safely disconnected from your computer.
2. Turn off any connected devices, such as monitors or speakers, by pressing their respective power buttons.
Remember, it’s important to shut down and disconnect devices properly to prevent any potential damage or malfunctions. If you’re experiencing blue screen errors or other system problems, consider updating your drivers or seeking further assistance from the Blue Screen Troubleshooter or Microsoft’s support sources.
Restarting in Safe Mode
To restart your PC in Safe Mode and resolve Windows BSoD errors, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key and R simultaneously to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “msconfig” and press Enter to open the System Configuration window.
3. In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab.
4. Under the Boot options section, check the box next to “Safe boot” and select “Minimal”.
5. Click OK and then click Restart when prompted.
6. Your computer will now restart in Safe Mode, where only essential drivers and services are loaded.
7. Once in Safe Mode, you can troubleshoot and fix any issues causing the Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) errors.
8. To exit Safe Mode, open the System Configuration window again and uncheck the “Safe boot” option.
9. Click OK and then restart your PC.
If you’re unable to resolve the issue or need further assistance, Microsoft Support is available to help.
Uninstalling Recently Installed Programs
To uninstall recently installed programs on your PC and resolve Windows BSoD errors, follow these steps:
1. Go to the Start menu and open the Control Panel.
2. Click on “Uninstall a program” under the “Programs” section.
3. A list of installed programs will appear. Look for the program you want to uninstall.
4. Right-click on the program and select “Uninstall” from the drop-down menu.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation process.
6. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
If you’re still experiencing BSoD errors after uninstalling the program, it may be caused by other factors. Consider updating your drivers or seeking further assistance from Microsoft’s customer support. Remember to provide them with any relevant information, such as error codes or the specific problem you’re facing.
Rollback or Disable Drivers
To rollback or disable drivers on your PC to resolve Windows BSoD errors, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + X and select Device Manager from the menu.
2. In the Device Manager window, expand the category of the device whose driver you want to rollback or disable.
3. Right-click on the device and select Properties.
4. Go to the Driver tab and click on Roll Back Driver if available. This will revert the driver to a previous version.
5. If the Roll Back Driver option is greyed out, click on Disable Device instead. This will temporarily disable the driver.
6. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
By rolling back or disabling drivers, you can troubleshoot and fix BSoD errors caused by incompatible or faulty drivers. If you still encounter issues, consider updating your drivers or seeking further assistance from Microsoft’s support.
Scanning for Malware and Running SFC Scan
To fix Windows BSoD errors, it’s crucial to scan for malware and run an SFC (System File Checker) scan. Here’s how to do it:
1. Scanning for Malware:
– Open Windows Security by clicking on the Start menu, selecting Settings, and then clicking on Update & Security.
– In the Windows Security window, select Virus & Threat Protection.
– Click on Quick Scan or Full Scan to check for any malware or viruses on your computer.
– Follow the on-screen instructions to remove any detected threats.
2. Running SFC Scan:
– Press the Windows key + X and select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
– Type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter.
– The SFC scan will initiate and check for any corrupt system files. If any issues are found, they will be repaired automatically.
Remember, regularly scanning for malware and running SFC scans can help resolve Windows BSoD errors and keep your computer running smoothly. If you need further assistance, don’t hesitate to Get Help from Microsoft support.
Checking Computer’s RAM and Hard Drive
To check your computer’s RAM and hard drive for potential issues, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “mdsched.exe” and press Enter to open the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool.
3. Choose either to restart now and check for problems or to check for problems the next time you restart your computer.
4. The tool will scan your computer’s RAM for errors and provide a detailed report if any issues are found.
To check your hard drive for errors, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + E to open File Explorer.
2. Right-click on the drive you want to check (typically the C: drive) and select Properties.
3. Go to the Tools tab and click on “Check” under the Error checking section.
4. Select “Scan drive” to begin the process.
5. The tool will scan your hard drive for errors and attempt to fix them if possible.
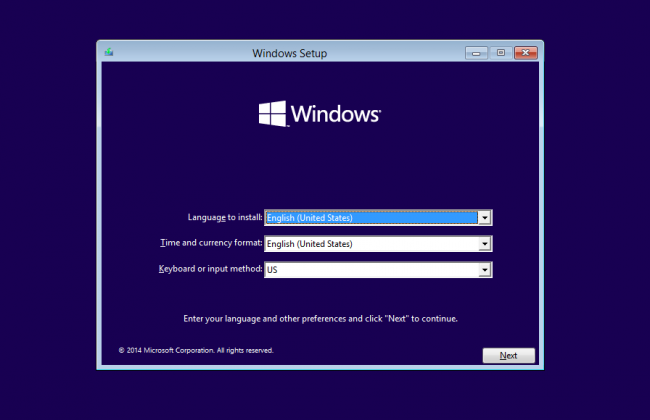
Last Resort: Reinstalling Windows
If you’ve exhausted all other options and are still experiencing Windows Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) errors, reinstalling Windows may be your last resort solution. Follow these steps to reinstall Windows:
1. Backup your important files and data to prevent any loss during the reinstallation process.
2. Insert your Windows installation media (USB or DVD) and restart your PC.
3. Press any key to boot from the installation media.
4. Select your language preferences and click “Next”.
5. Click “Install now” and follow the on-screen instructions to proceed.
6. When prompted, choose “Custom installation” and select the drive where you want to reinstall Windows.
7. Let the installation process complete, and your PC will restart several times.
8. After the installation is finished, set up your Windows account and customize your settings.
9. Restore your backed-up files and reinstall your apps.
Remember to regularly update your drivers and keep your operating system up to date to prevent future BSoD errors. If you need further assistance, reach out to Microsoft Support for help.








