Unraveling the intricate mechanisms behind a system restore: demystifying the enigmatic process that occasionally leads to data loss.
Recently, Fortect has become increasingly popular as a reliable and efficient way to address a wide range of PC issues. It's particularly favored for its user-friendly approach to diagnosing and fixing problems that can hinder a computer's performance, from system errors and malware to registry issues.
- Download and Install: Download Fortect from its official website by clicking here, and install it on your PC.
- Run a Scan and Review Results: Launch Fortect, conduct a system scan to identify issues, and review the scan results which detail the problems affecting your PC's performance.
- Repair and Optimize: Use Fortect's repair feature to fix the identified issues. For comprehensive repair options, consider subscribing to a premium plan. After repairing, the tool also aids in optimizing your PC for improved performance.
Understanding System Restore
System Restore is a powerful feature in Windows 10 that allows you to revert your computer’s state to a previous point in time. It can be a lifesaver when your PC encounters problems or you accidentally delete important files.
To perform a System Restore, follow these steps:
1. Open the Start menu and type “System Restore” in the search bar.
2. Click on “Create a restore point” from the list of options.
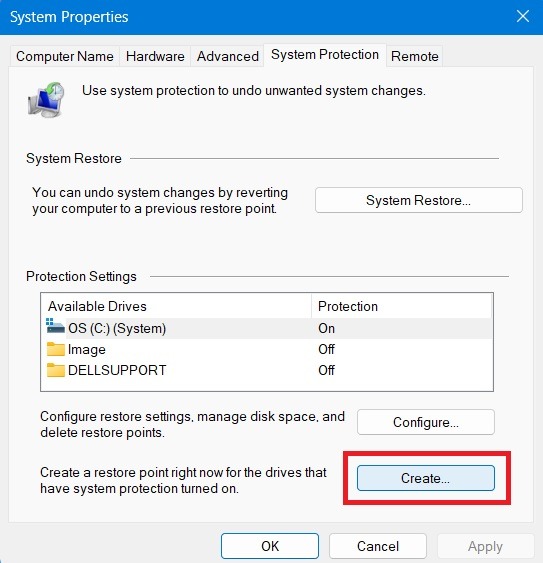
3. In the System Properties window, click the “System Restore” button.
4. Select a restore point from the list and click “Next.”
5. Review the details and click “Finish” to start the restore process.
Note that System Restore will not affect your personal files, but it may uninstall recently installed programs or updates. It’s always a good practice to backup your important files before performing a System Restore.
If you encounter any issues or receive a restore error, you can try using the Command Prompt to recover files or reset Windows. It’s important to note that System Restore may not always complete successfully, especially if there is not enough disk space or system protection is disabled.
Using System Restore to Recover Deleted Files
If you accidentally deleted important files on your PC, System Restore can be a lifesaver. Here’s how to recover them:
1. Open the Start menu and search for “System Restore.”
2. Click on “Create a restore point” in the results.
3. In the System Protection tab, click on the “System Restore” button.
4. Select a restore point before the files were deleted and click “Next.”
5. Review the details and click “Finish” to start the restore process.
6. Your computer will restart, and the files should be restored to their previous state.
Creating and Restoring System Restore Points
To create a System Restore Point in Windows 10, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Start button.
2. In the search bar, type “Create a restore point” and select the option that appears.
3. In the System Properties window, click on the “Configure” button.
4. Select the “Turn on system protection” option and adjust the disk space usage according to your needs.
5. Click on “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
To restore your system to a previous point:
1. Open the System Properties window again.
2. Click on the “System Restore” button.
3. Follow the instructions in the Restore system files and settings window.
4. Select a restore point and click on “Next”.
5. Review the information and click on “Finish” to start the restoration process.
python
import os
def list_files(directory):
files = []
for root, _, filenames in os.walk(directory):
for filename in filenames:
files.append(os.path.join(root, filename))
return files
def compare_files(original_files, restored_files):
lost_files = set(original_files) - set(restored_files)
return lost_files
# Provide the paths to the original and restored directories
original_directory = '/path/to/original'
restored_directory = '/path/to/restored'
# Get the list of files in the original and restored directories
original_files = list_files(original_directory)
restored_files = list_files(restored_directory)
# Compare the files to identify any lost files
lost_files = compare_files(original_files, restored_files)
# Print the lost files, if any
if lost_files:
print("The following files might have been lost:")
for file in lost_files:
print(file)
else:
print("No files were lost after the system restore.")
Common Issues and FAQs about System Restore
- What is System Restore? – Learn about the purpose and functionality of System Restore on your computer.
- How does System Restore work? – Understand the underlying process of how System Restore functions to restore your system to a previous state.
- Can System Restore cause data loss? – Discover the potential risks associated with performing a System Restore and its impact on your personal files.
- What types of issues can System Restore resolve? – Find out the common problems that System Restore can effectively address.

- How far back can I restore my system? – Learn about the time range available for selecting a restore point.
- Will System Restore affect my installed programs? – Understand the impact of a System Restore on your software applications and configurations.
- Can I undo a System Restore? – Explore the options available for reversing a System Restore process.
- Are there any limitations to System Restore? – Discover any constraints or restrictions associated with using System Restore.
- Is it necessary to create a backup before using System Restore? – Understand the importance of having a backup strategy in place.
- How long does System Restore take? – Get an idea of the time required to complete a System Restore operation.

Troubleshooting System Restore Problems
If you’re experiencing issues with System Restore, here are some helpful tips to get you back on track:
1. Check System Restore points: Before troubleshooting, ensure that you have valid restore points available.
2. Run System Restore in Safe Mode: Boot your computer into Safe Mode and try running System Restore from there.
3. Disable antivirus and security software: Temporarily disable any antivirus or security software that may interfere with the restore process.
4. Use an elevated Command Prompt: Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the “sfc /scannow” command to scan and repair system files.
5. Check disk errors: Use the “chkdsk” command to check for and fix any disk errors that may be causing the restore failure.
6. Recover files using File History or a backup: If the restore did not complete successfully, you can still recover your important files using File History or a backup.
7. Reset Windows: In extreme cases, you may need to perform a factory reset of your PC to resolve system restore errors.
Remember, if you’re unsure about any step or encounter any issues, don’t hesitate to reach out to Microsoft Support for further assistance.
For more detailed instructions, please refer to the Microsoft support article [link to article].
Disadvantages of Using System Restore
1. Potential loss of data: System Restore can lead to the loss of recent files, documents, and applications that were created or installed after the restore point was created. It’s important to back up important files before proceeding.
2. Restores all settings: System Restore reverts your computer’s settings, including installed software and system configurations, back to a previous state. This means any changes or updates made to your operating system or programs will be undone.
3. Doesn’t fix all problems: While System Restore can resolve certain software issues, it may not always fix complex hardware or driver-related problems. In some cases, a more comprehensive solution may be required.
4. Restore errors: There is a possibility of encountering errors during the System Restore process, such as a “restore failed” or “restore did not complete successfully” message. These errors can prevent your computer from being restored to a previous state.
5. No guarantee for deleted files: System Restore does not provide a guarantee for recovering deleted files. While it may be able to restore some deleted files, it’s not a reliable backup solution. It’s always recommended to regularly back up important files to avoid permanent data loss.
6. Factory reset: If your computer is in a severely compromised state, a factory reset may be a more effective solution than System Restore. This will completely reinstall the operating system and restore your computer to its original settings, eliminating any persistent issues.